Why are consumers willing to pay more for a well-known brand product than buy a more affordable alternative from a company without a big name?
According to statistics 60% of consumers would choose the trusted brand over a cheaper alternative.
Purchasing decisions come from exposure to marketing messages, advertising, PR, and ‘social proof that ultimately lead us to conclude if one is better than the other.
It’s all about brand equity and how well you communicate the product’s values to your audience. In this article, we explain what brand equity is, why it is important to a brand, and how to measure it.
What is brand equity?
Brand equity is the level of sway a brand has in the minds of consumers and the level of positive value that a consumer perceives in a brand compared with other brands. When offered a drink in a restaurant, rather than say water, what do you say?
Strong brand equity makes it easier for a business to stay ahead of the competition, attract and retain customers, and launch new products to market.
To create brand equity, you need to provoke positive associations with your brand and create value that can make customers choose your product and be willing to pay more than another product. Make them pay for the brand.
Because with strong brand equity, it is easier for a business to stay ahead of the competition, attract and retain customers, and launch new products to market.
What are the components of brand equity?
– Brand Recognition / Brand Awareness
Customer knowledge of your brand and products is an important part of brand equity.
Do consumers know about your brand, and can they distinguish it from other similar brands in the market? Raising awareness is one of the most important steps for a business to increase sales.
Some methodologies used to understand how aware your customers include:
– Surveys and focus groups
– Search volume for your brand and products
– Media mentions
– Social mentions and reviews
– Brand perception
Brand perception refers to the way that consumers perceive and interpret a brand. It encompasses all the feelings and thoughts of the consumer about the values, qualities, and characteristics of the brand.
Note that how people feel about the brand and their perception may differ from the actual positioning of the brand.
Positive brand perception can lead to increased sales, customer loyalty, and a solid competitive advantage, while negative brand perception can result in lost sales, damaged reputation, and reduced customer loyalty.
– Preference Metrics
Preference metrics are used to measure the degree to which customers prefer one brand, product, or service over another. These metrics are important because they provide valuable insights into customer preferences and help businesses better understand how to improve their offerings to meet customer needs and expectations.
There are several different types of preference metrics:
– Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty by asking customers how likely they are to recommend a brand or product to others on a scale of 0-10. Customers who score 9 or 10 are considered promoters, while those who score 0-6 are considered detractors.
– Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): CSAT measures customer satisfaction by asking customers to rate their satisfaction with a product or service on a scale of 1-5 or 1-10. The score is calculated by taking the percentage of customers who gave a rating of 4 or 5 (or 9 or 10) and dividing it by the total number of respondents.
– Customer Effort Score (CES): CES measures the ease of doing business with a company by asking customers how easy it was to complete a specific task or transaction. The score is calculated by taking the percentage of customers who found the task or transaction easy and subtracting the percentage who found it difficult.
– Brand Preference: Brand preference measures the degree to which customers prefer one brand over another. This can be measured through surveys that ask customers which brand they would choose in a specific situation or by tracking customer purchase behavior over time.
– Attribution, or consideration for use
Attribution, or consideration for use, refers to the degree to which a customer is considering or willing to use a particular product or service. Customers know the basic attributes of the brand. It’s all the product components that the customer can see and talk about. Each industry and brand will have its attributes – without them, customers will not buy your products.
Why is Brand Equity Important?
Brand equity is important for a number of reasons. First, strong brand equity helps increases customer loyalty. Consumers are more likely to choose a brand they know and trust.
Another reason is higher perceived value. Brands with strong equity can often command higher prices for their products or services, as consumers perceive them as having greater value.
Organizations that leverage the power of branding often earn more money than competitors while spending less. For example, positive brand equity enables brands to charge premium prices. When consumers believe in the values put forth by a brand and the quality of its products, they will pay higher costs to purchase from that brand.
One of the main tasks in working with a brand is to understand how all the efforts made by the brand team affect financial performance. With brand equity metrics, you can see the result of working on a brand.
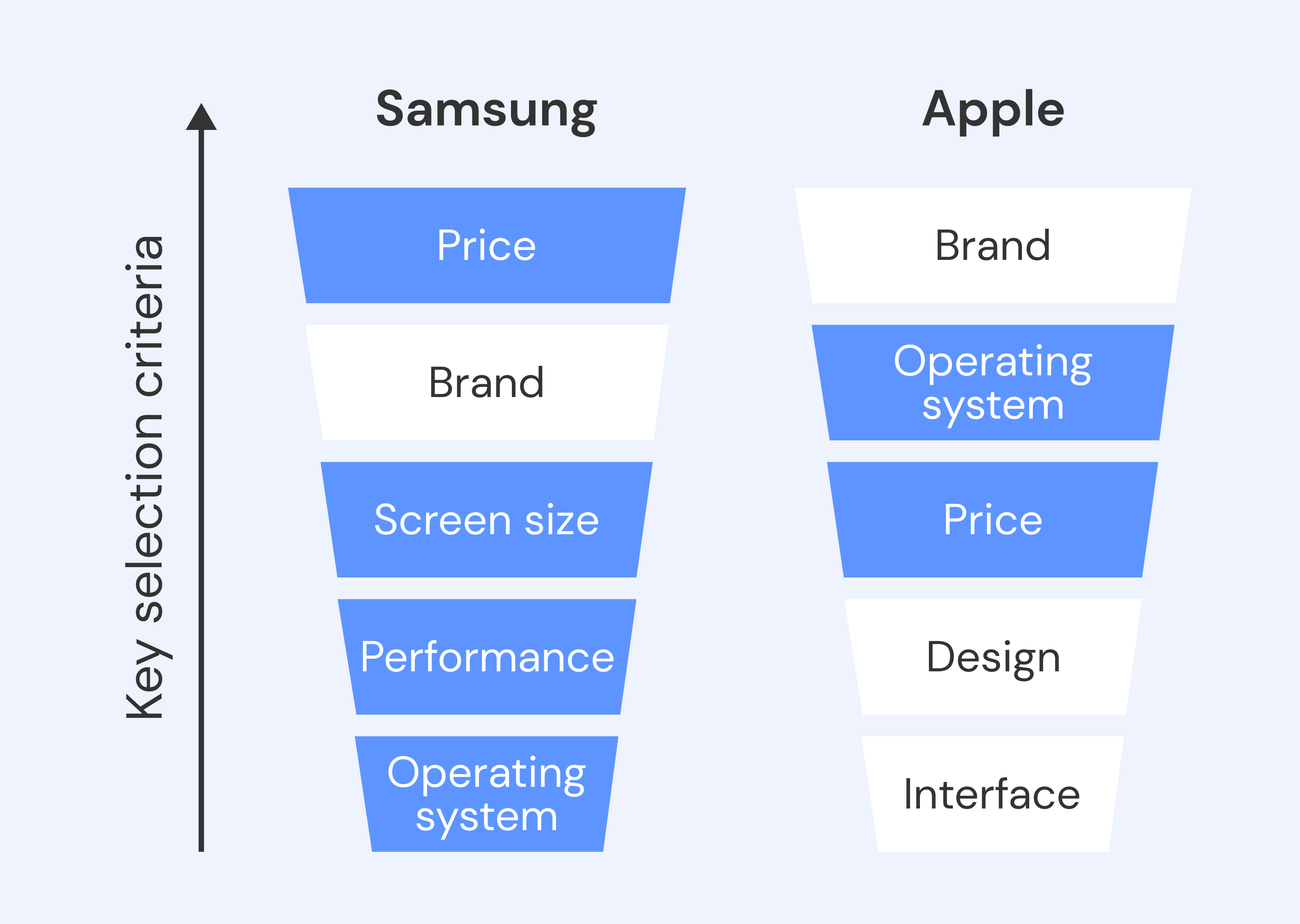
Let’s see the example – Samsung and Apple. What are the things you consider when choosing a phone? For Samsung, the price comes first, then the brand, and then the functional attributes.
For Apple, the brand ranks first. A strong brand helps a company generate added value, leading to premium market positioning and higher product value.
How to measure brand equity?
A brand is, by nature, a difficult concept to measure, as there is no single or consistent metric that brands can use to measure consumers’ subjective responses and emotions.
However, it remains an essential function, as losing sight of the strength of value can affect results and the ability to compete.
So, we’ve described one of the ways you can keep track of your brand’s strength.
– Step 1
Define your brand attribution
Brand attributes characterize your brand without looking at what you do or sell. It’s the core values and characteristics — your brand’s personality traits. It’s what consumers see when looking at your brand as a whole.
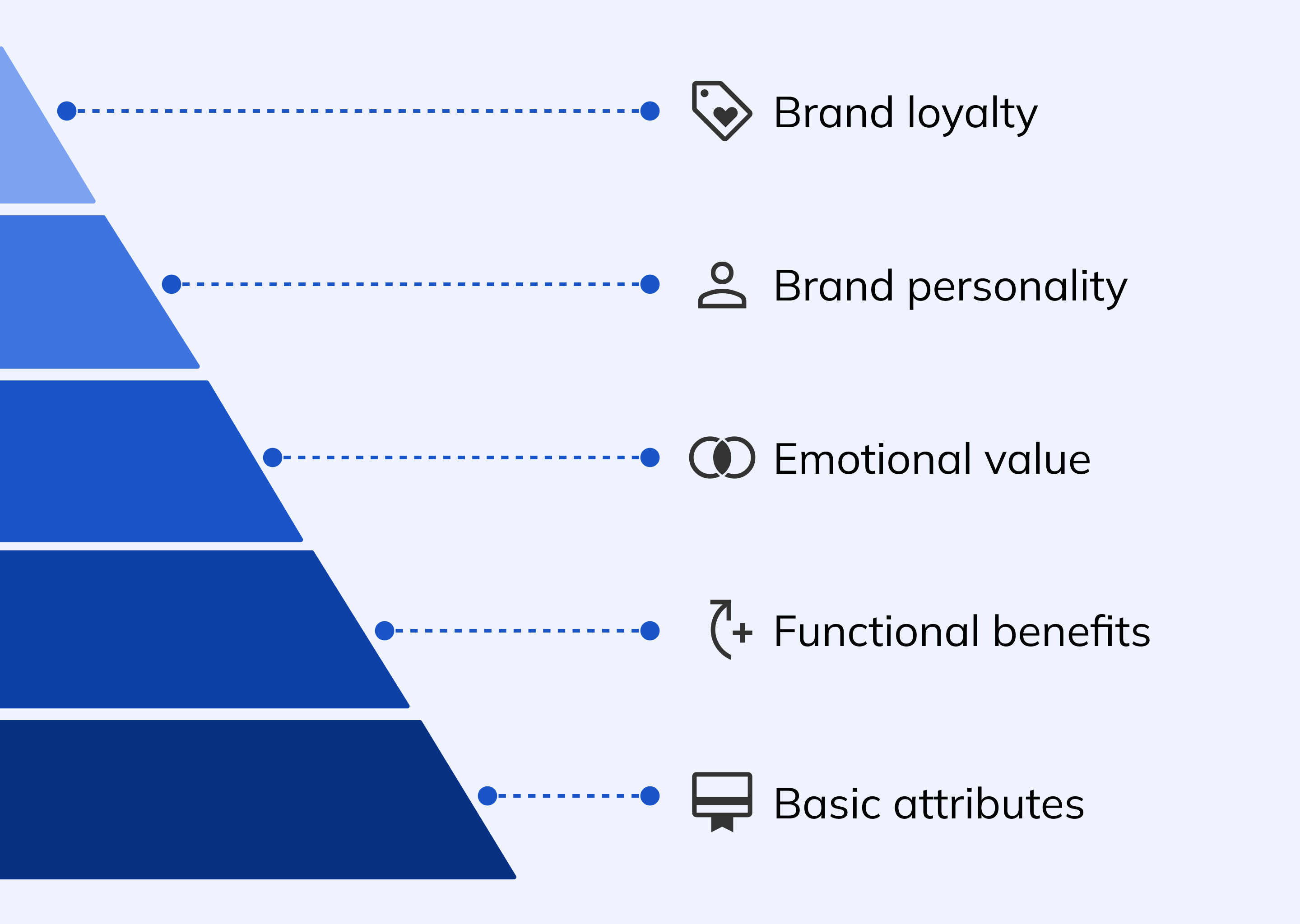
Before calculating brand equity, it is important to determine the sources of brand value or attribution. This involves identifying a brand’s specific attributes or characteristics that contribute to its overall value and impact in the market. Let’s split brand attributes into three categories to make them less abstract.
Basic attributes create the first impression of a brand and help make an emotional connection between the company and customers. Usually, the basic attributes include the name, logo, corporate colors, and fonts.
Functional brand attributes are the specific characteristics of your brand that contribute to its functional or practical benefits for customers. These attributes are directly tied to the features and benefits of your products or services and help differentiate your brand from competitors. For example, it could be a unique technology, like Dyson vacuum cleaners, that allows people not to change the dust bag.
Image brand attributes are the emotional and psychological characteristics that customers associate with your brand. Such attributes help the audience build a clearer understanding and association with the brand and the core values for customers. In addition, these attributes help create a positive perception of your brand in customers’ minds and contribute to their overall impression of your brand.
To calculate brand equity, you need to determine how important each attribute is for the audience. To find out, you can conduct a survey and ask respondents how important a certain characteristic is when choosing a company without mentioning the brand.
The answers will allow you to prioritize, give each attribute weight, and use it during competitors’ research.
Here is an example of brand attributes you’ll recognize,
Apple
Apple’s brand attributes are all about lifestyle. You don’t just have an iPhone, you’re an Apple user. In their messaging, imagination and innovation are important. They focus on creativity and shaping technology to benefit human needs. That focus becomes clear in their designs: an iPhone billboard usually only shows, well, an iPhone. No crazy fonts, funny copy — it’s about the technology — and about you. They are incredibly product-focused and their simplicity is easy to recognize. You’ll remember the product, not some jingle.
– Step 2
Calculate Brand Equity Index
BEI = (percentage of people who know the brand / 100) * (percentage of people who identify the most significant attribute of the brand / 10) + (number of image attributes of the brand)
This formula is used to calculate Brand Equity Index (BEI) which is a measure of the value of a brand in the marketplace. The formula takes into account both functional and image attributes of the brand. The percentage of people who know the brand is multiplied by the percentage of people who identify the most significant attribute of the brand and then divided by 10. This is added to the number of image attributes of the brand to get the overall BEI score. The higher the BEI score, the more valuable the brand is in the marketplace.
To sum up,
Brand equity represents extremely important for any business and includes the knowledge that the consumer has of it, the associations it makes with the brand and the degree of loyalty of consumers.
Also, brand equity is an important component of marketing strategies, as it significantly impacts a brand’s ability to maintain long-term competitive advantage.